In today’s fast-paced industries, managing wastewater efficiently is a critical concern, especially for residential societies. With increasing population density and water consumption, untreated sewage poses significant environmental and health hazards. A Sewage Treatment Plant for Residential Society is an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution to ensure the safe disposal and reuse of wastewater. This blog explains the importance, benefits, and implementation of sewage treatment plants (STP) in residential societies.
Sewage Treatment in Residential Building
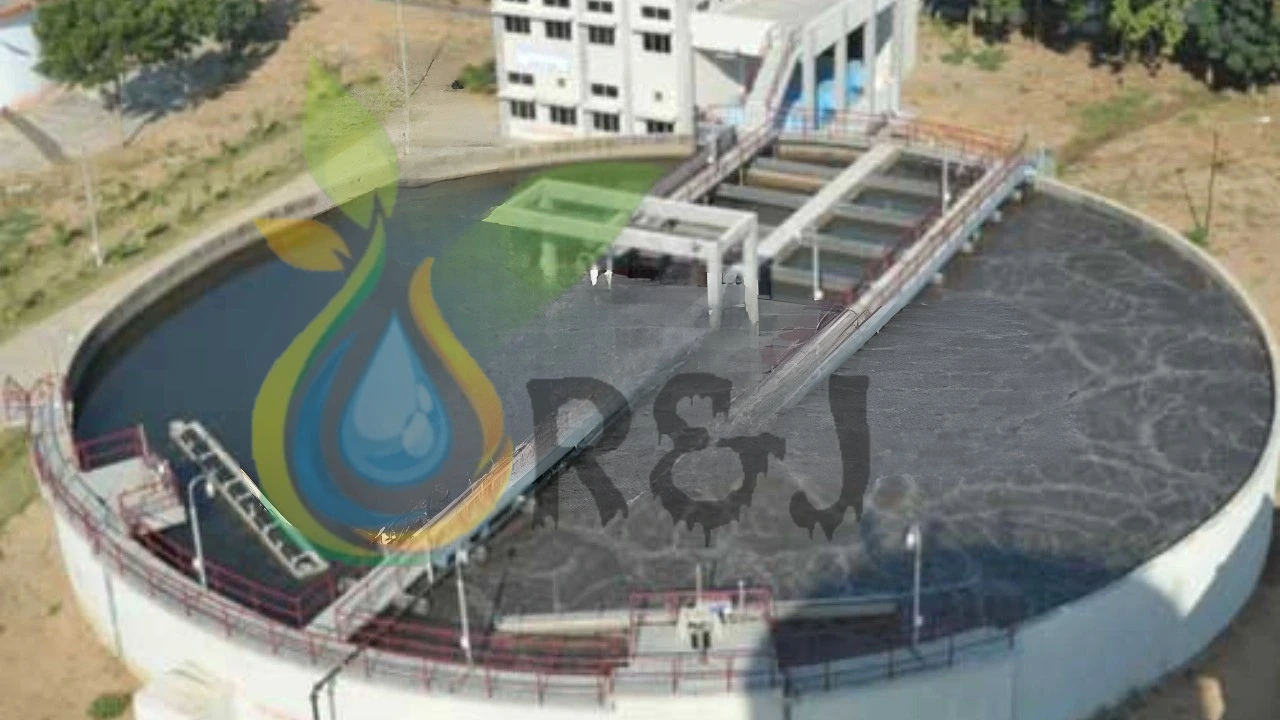
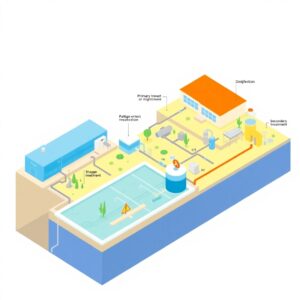
Sewage Treatment Plant for Residential Society is an essential water treatment solution designed to treat and recycle wastewater generated from households, kitchens, and bathrooms in apartments or housing complexes. As residential societies produce a large volume of sewage every day, direct disposal into the environment can cause serious pollution. An STP Plant for residential society ensures this wastewater is treated, purified, and reused.
Read More : LPH in RO Water Purifier
Benefits of Sewage Treatment Plant for Residential Society
- Environmental Protection – Prevents untreated sewage from polluting lakes, rivers, and groundwater.
- Water Reuse – Treated water can be reused for gardening, toilet flushing, and cleaning, reducing fresh water consumption.
- Regulatory Compliance – Meets Pollution Control Board (PCB) norms and avoids penalties.
- Odour & Hygiene Control – Proper treatment prevents foul smell, mosquito breeding, and health hazards.
- Sustainable Living – Encourages eco-friendly practices and supports water conservation.
- Increased Property Value – Well-managed societies with STPs are more attractive to buyers and residents.
- Community Welfare – Improves overall quality of life by ensuring a clean, green, and healthy living environment.
R&J wastewater treatment Organization is a leading sewage treatment plant manufacturer, we offer best quality sewage treatment plant for residential buildings, offered in various capacities or designs for different applications. We always focused on the quality standard and reliability of our STP Plant for residential building. Our team ensures that our product performs well in their applications.