Welcome to R&J Waste Water Treatment Organization, your trusted partner in sustainable water management. Today, we’re diving into an essential topic: How Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) Work. We’ll break down the process into simple steps and include a clear diagram to make it easy to understand. A sewage treatment plant is a facility that receives waste from residential, commercial, and industrial sources and removes contaminants that harm water quality and endanger public health and safety when discharged into receiving systems or on land. It is a collection of unit operations and unit procedures designed to treat sewage to desirable standards in accordance with regulating authority effluent requirements.
What is a Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)?
A Sewage Treatment Plant is a facility designed to remove contaminants from wastewater, primarily household sewage. The goal is to produce water that is safe for the environment and can be reused or safely discharged. STPs play a crucial role in protecting water bodies from pollution.
The Sewage Treatment Process
There are 5 stages in a wastewater treatment plant:
1. Preliminary Treatment
This stage focuses on removing large solids and debris from the sewage. The main components include:
- Screens: To trap large objects like sticks, rags, and plastics.
- Grit Chamber: Removes sand, gravel, and other heavy particles.
2. Primary Treatment
In this stage, the wastewater flows into a sedimentation tank where:
- Suspended solids settle at the bottom to form sludge.
- Grease and oils float to the surface and are skimmed off.
3. Secondary Treatment
This is the biological phase where microorganisms break down organic matter. Common methods include:
- Activated Sludge Process: Aeration tanks supply oxygen to encourage microbial growth.
- Trickling Filters: Wastewater passes through beds of stones or plastic, where microbes consume organic matter.
4. Tertiary Treatment
The final stage involves polishing the water to remove remaining impurities. Techniques include:
- Filtration: Removes fine particles.
- Disinfection: Kills harmful pathogens using chlorine, UV light, or ozone.
- Nutrient Removal: Reduces nitrogen and phosphorus levels.
5. Sludge Treatment
The sludge collected during primary and secondary treatment undergoes further processing to reduce volume and produce useful by-products. This includes:
- Thickening and Dewatering: Removes excess water.
- Anaerobic Digestion: Converts organic material into biogas.
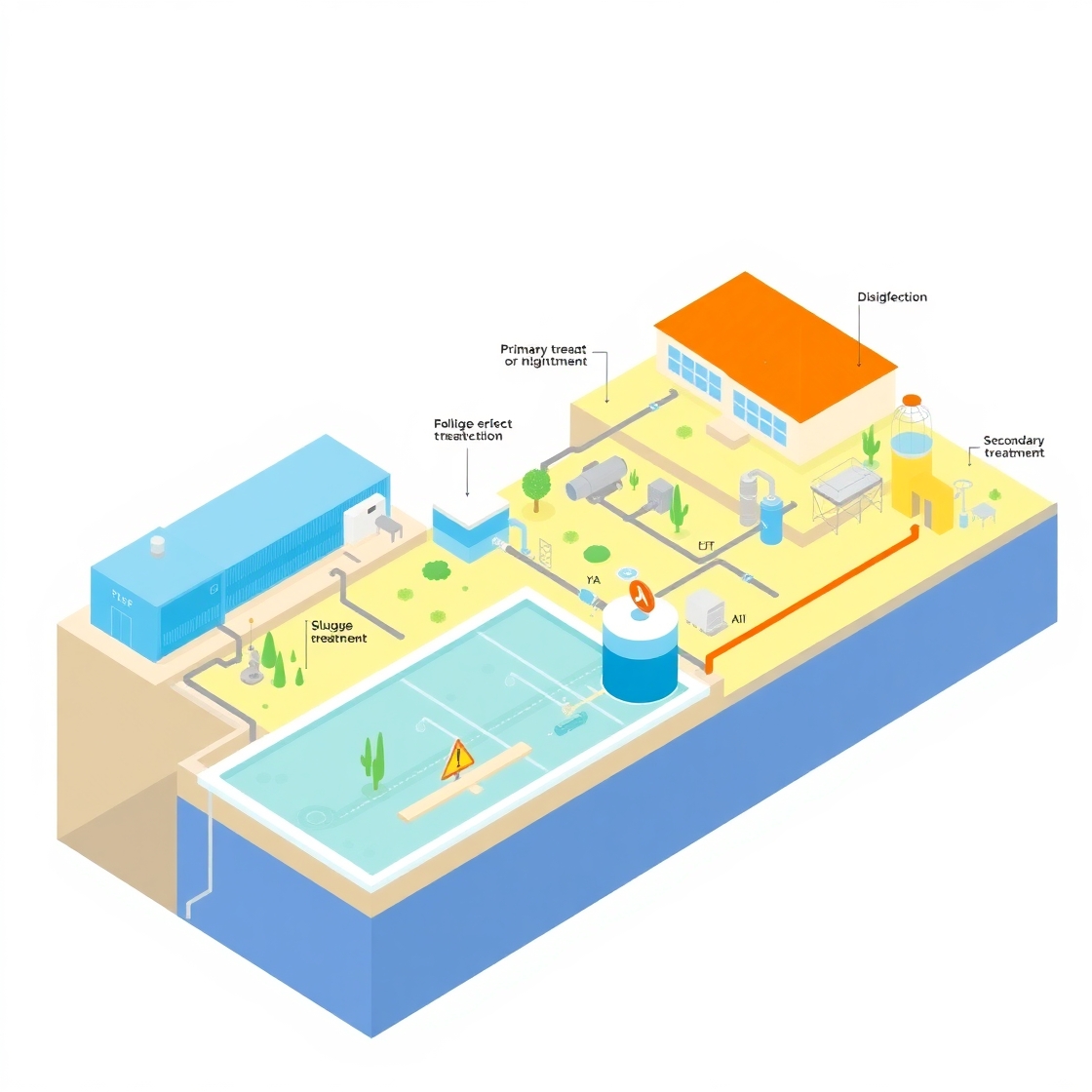
sewage treatment plant diagram with explanation
Below is a simplified diagram of the sewage treatment process:

Sewage treatment plants are facilities designed to treat wastewater from domestic, commercial, and industrial sources. The treatment process involves removing contaminants and pollutants from the water to make it safe for discharge into the environment or for reuse. The treatment of sewage typically involves four main stages:
- Primary Treatment in Sewage Treatment Plant
- Secondary Treatment in Sewage Treatment Plant
- Tertiary Treatment in Sewage Treatment Plant
- Sludge Treatment in Sewage Treatment Plant
Why Choose R&J Waste Water Treatment Organization?
At R&J, we specialize in designing, installing, and maintaining efficient sewage treatment systems. Our expert team ensures compliance with environmental regulations while delivering cost-effective solutions. By choosing us, you’re contributing to a cleaner, greener future.
Conclusion
Understanding how sewage treatment plants work is vital for appreciating their role in protecting our environment. If you’re interested in learning more or need a customized STP for your facility, don’t hesitate to contact us at R&J Waste Water Treatment Organization. Together, we can ensure a sustainable tomorrow.
Contact Us
For inquiries, reach out via our website or call us at [+91 7017079891].